This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Neural Networks, Tensors and other stuff
Formats
| Safetensors | Safe store for tensors |
| GGUF | Georgi Gerganov Universal Format (it can mix various precisions) |
| PT | PyTorch format |
Quantization
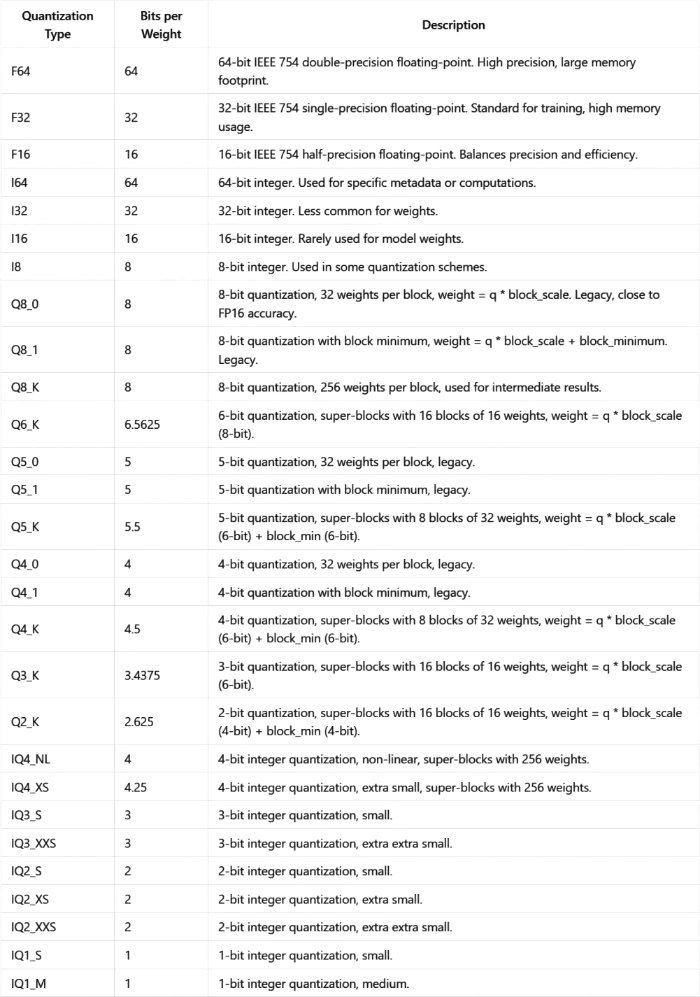
| Quantization Type | Bits per Weight | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FG4 | 64 | 64-bit IEEE 754 double-precision floating-point. High precision, large memory footprint. |
| F32 | 32 | 32-bit IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point. Standard for training, high memory usage. |
| F16 | 16 | 16-bit IEEE 754 half-precision floating point. Balances precision and efficiency. |
| I64 | 64 | 64-bit integer. Used for specific metadata or computations. |
| I32 | 32 | 32-bit integer. Less common for weights. |
| I16 | 16 | 16-bit integer. Rarely used for model weights. |
| I8 | 8 | 8-bit integer. Used in some quantization schemes. |
| Q8_0 | 8 | 8-bit quantization, 32 weights per block, weight = q * block_scale, legacy, close to FP16 accuracy. |
| Q8_1 | 8 | 8-bit quantization with block minimum, weight = q * block_scale + block_minimum, legacy. |
| Q8_K | 8 | 8-bit quantization, 256 weights per block, used for intermediate results. |
| Q6_K | 6.5625 | 6-bit quantization, super-blocks with 16 blocks of 16 weights, weight = q * block_scale (8-bit). |
| QS 0 | 5 | 5-bit quantization, 32 weights per block, legacy. |
| QS_1 | 5 | 5-bit quantization with block minimum, legacy. |
| QS_K | 5.5 | 5-bit quantization, super-blocks with 8 blocks of 32 weights, weight = q * block_scale (6-bit) + block_min (6-bit). |
| Q4_0 | 4 | 4-bit quantization, 32 weights per block, legacy. |
| Q4_1 | 4 | 4-bit quantization with block minimum, legacy. |
| Q4_K | 4.5 | 4-bit quantization, super-blocks with 8 blocks of 32 weights, weight = q * block_scale (6-bit) + block_min (6-bit). |
| Q3_K | 3.4375 | 3-bit quantization, super-blocks with 16 blocks of 16 weights, weight = q * block_scale (6-bit). |
| Q2_K | 2.625 | 2-bit quantization, super-blocks with 16 blocks of 16 weights, weight = q * block_scale (4-bit) + block_min (4-bit). |
| IQ4_NL | 4 | 4-bit integer quantization, non-linear, small super-blocks with 256 weights. |
| Q2_K | 4 | 4-bit integer quantization, extra small, super-blocks with 256 weights. |
| I16_NL | 3 | 3-bit integer quantization, small. |
| I8_NL | 3 | 3-bit integer quantization, small. |
| Q4_K | 4 | 4-bit quantization, extra small, super-blocks with 32 weights. |
| Q2_K | 2 | 2-bit integer quantization, extra small. |
| I8_NL | 3 | 3-bit integer quantization, medium. |
| I4_NL | 2 | 2-bit integer quantization, medium. |
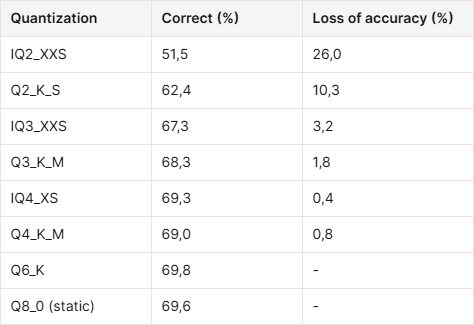
Approx. loss
Legacy Quantizations (Q4_0, Q4_1, Q5_0, Q5_1, Q8_0, Q8_1): These are simpler, faster methods but may have higher quantization error compared to newer types.
K-Quantizations (Q2_K, Q3_K, Q4_K, Q5_K, Q6_K): Introduced in llama.cpp PR #1684, these use super-blocks for smarter bit allocation, reducing quantization error.
I-Quantizations (IQ2_XXS, IQ3_S, etc.): State-of-the-art for low-bit widths, using lookup tables for improved accuracy but potentially slower on older hardware.
GGUF Q8_0: Very close to FP16 (perplexity 7.4933), indicating minimal accuracy loss.
GGUF Q4_K_M: Slightly higher perplexity (7.5692), still usable for most tasks.
Opensource llm models
| Model | Maker |
|---|---|
| Gemma 3 | |
| Nemotron | NVIDIA |
| LLama 3 | |
| DeepSeek | DeepSeek |
| Qwen | Alibaba |
| Mistral | Mistral AI |
Opensource visual models
Stable Diffusion 1
Stable Diffusion XL
Stable Diffusion 3
by Stability AI https://stability.ai
Flux.1d
by Black Forest Labs https://bfl.ai
HiDream I1
Qwen
CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training)
Self-attention Transformer as a text encoder